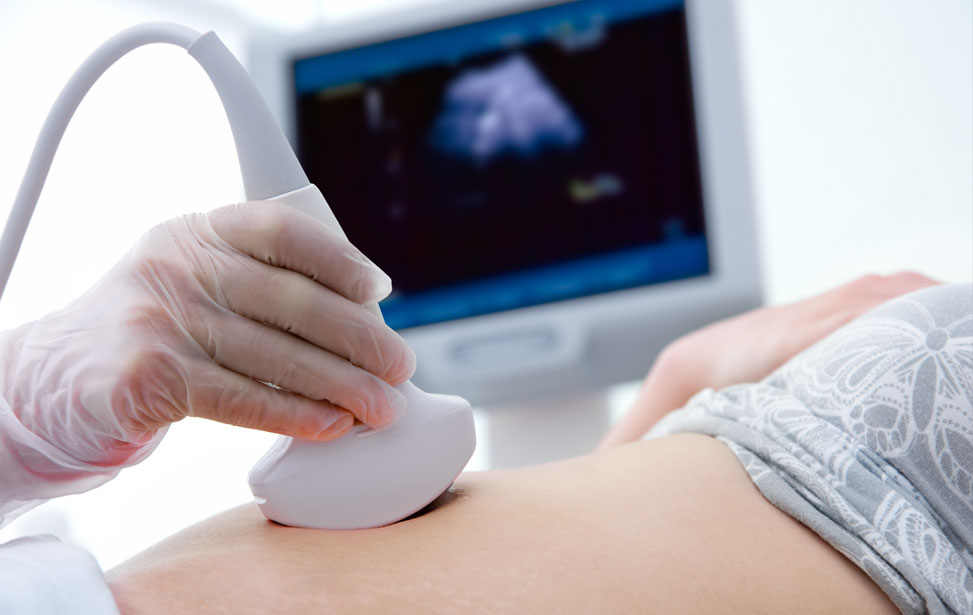
Sonography
Sonography, also known as ultrasound imaging, is a non-invasive medical imaging technique that utilizes high-frequency sound waves to create real-time images of the internal structures of the body. This technology is widely used in various medical fields, including obstetrics, cardiology, and abdominal diagnostics. Sonography is a valuable tool for assessing organ health, detecting abnormalities, and guiding certain medical procedures.
During a sonography procedure, a small device called a transducer is placed on the skin over the area of interest. The transducer emits sound waves that bounce off internal tissues and organs, producing echoes that are converted into visual images on a monitor. The entire process is painless, typically taking about 20 to 30 minutes, and requires no special preparation in most cases. Sonography is particularly popular for monitoring pregnancies, as it provides essential information about the developing fetus and the health of the mother.
Sonography can be classified into various types based on its application. Obstetric sonography is used to monitor fetal development during pregnancy, while abdominal sonography examines organs such as the liver, gallbladder, kidneys, and pancreas. Cardiac sonography, or echocardiography, focuses on evaluating heart function and structure. Doppler sonography assesses blood flow in vessels, helping to diagnose conditions such as vascular blockages or blood clots.
One of the key advantages of sonography is its safety. Unlike X-rays or CT scans, sonography does not involve ionizing radiation, making it a preferred imaging method, especially for pregnant women and children. Additionally, sonography is versatile and can be performed at the bedside, in outpatient clinics, or in hospital settings, enhancing its accessibility for patients.
While sonography is a highly effective diagnostic tool, it does have limitations. The quality of images can be affected by factors such as obesity, bowel gas, or the presence of certain medical conditions. In some cases, additional imaging studies may be required to provide a comprehensive evaluation. However, ongoing advancements in ultrasound technology, including 3D and 4D imaging, continue to improve the clarity and accuracy of sonographic assessments.
In conclusion, sonography is an essential imaging modality that plays a critical role in modern medicine. Its non-invasive nature, safety, and versatility make it invaluable for diagnosing a wide range of medical conditions. Regular use of sonography contributes significantly to patient care by enabling timely detection and management of various health issues.
- Non-Invasive: Sonography is a safe and painless imaging technique, suitable for patients of all ages.
- Real-Time Imaging: Provides immediate visualization of internal structures, aiding in quick diagnosis and treatment decisions.
- Diverse Applications: Utilized in various medical fields, including obstetrics, cardiology, and abdominal diagnostics.
- No Radiation Exposure: Unlike other imaging methods, sonography does not use ionizing radiation, making it safer for vulnerable populations.