Echo Cardiography
Echo cardiography, commonly referred to as an "echo," is a non-invasive diagnostic imaging technique used to assess the structure and function of the heart. This test uses high-frequency sound waves (ultrasound) to create detailed images of the heart's chambers, valves, and blood flow. Echo cardiography is a valuable tool for diagnosing and monitoring a variety of heart conditions, such as heart valve disorders, congenital heart defects, cardiomyopathy, and heart failure. It provides real-time visual information about the heart's movements, enabling healthcare providers to evaluate the heart's pumping efficiency and detect abnormalities.
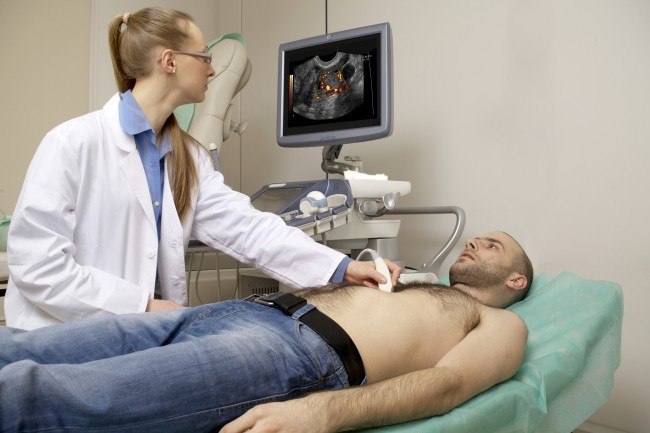
During an echo cardiography procedure, a small handheld device called a transducer is placed on the chest and moved over the heart area. The transducer emits sound waves that bounce off the heart structures and return as echoes, which are then converted into moving images displayed on a monitor. The procedure is painless and typically takes 30 to 60 minutes to complete. There are several types of echo cardiography, including **Transthoracic Echo (TTE)**, which is the most common and involves placing the transducer on the chest, and **Transesophageal Echo (TEE)**, where a specialized transducer is guided down the esophagus to provide a closer view of the heart. **Stress Echo** is performed while the heart is under stress, either through exercise or medication, to assess how it functions under increased workload.
Echo cardiography is recommended for individuals experiencing symptoms such as shortness of breath, chest pain, unexplained fatigue, or irregular heartbeats, as these can indicate underlying heart issues. It is also used to monitor patients with known heart conditions, assess the effectiveness of treatments, and guide surgical planning. For those with a history of heart disease or risk factors such as hypertension, diabetes, or high cholesterol, echo cardiography can help in early detection and intervention, reducing the risk of complications.
Several factors can influence the quality and accuracy of an echo cardiography, including body size, lung conditions, and the presence of certain medical devices. In such cases, a TEE may be recommended to obtain clearer images. Unlike X-rays or CT scans, echo cardiography does not involve radiation, making it a safe option for most patients, including pregnant women and children. It is essential, however, for patients to follow pre-test instructions, such as fasting or avoiding caffeine, to ensure accurate results.
One of the significant benefits of echo cardiography is its ability to provide comprehensive information about the heart's structure and function in real time. This allows healthcare providers to make informed decisions regarding diagnosis, treatment, and ongoing management of heart conditions. Echo cardiography is also a valuable tool for evaluating the effectiveness of medical or surgical treatments, helping to track improvements or identify the need for further interventions.
Despite its numerous advantages, echo cardiography has some limitations. It may not always provide clear images in individuals with obesity, lung disease, or those with certain anatomical variations. Additionally, while it can detect structural abnormalities and assess heart function, it may not always identify the cause of symptoms like chest pain or shortness of breath. Therefore, echo cardiography is often used in conjunction with other diagnostic tests, such as electrocardiograms (ECG) or cardiac MRI, for a more comprehensive evaluation of heart health.
In conclusion, echo cardiography is a vital and versatile tool in cardiology, providing detailed insights into heart structure and function. Its non-invasive nature, combined with its ability to detect and monitor a wide range of heart conditions, makes it an essential component of cardiovascular care, helping patients maintain optimal heart health and quality of life.
- Non-Invasive and Safe: Uses ultrasound, without radiation exposure, making it safe for most patients.
- Real-Time Heart Visualization: Provides live images of the heart's structure and function.
- Versatile Diagnostic Tool: Evaluates a wide range of heart conditions, from valve disorders to heart failure.
- Guides Treatment and Surgery: Assists in planning surgeries and monitoring treatment effectiveness.